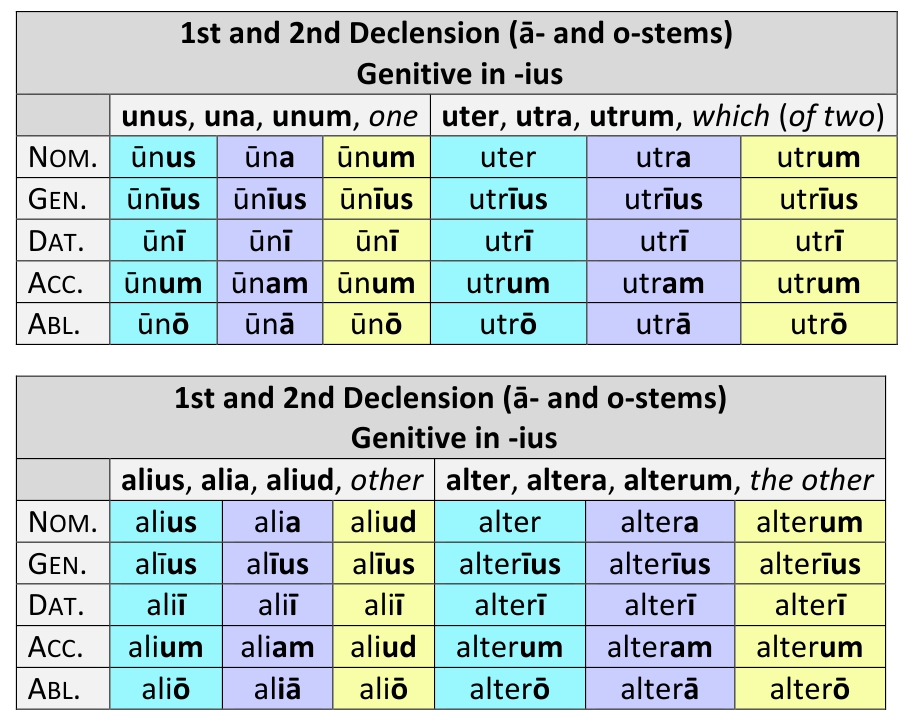
113. The following nine adjectives with their compounds have the Genitive Singular in -īus and the Dative in -ī in all genders.
| alius [aliud (n.)] other | tōtus whole | alter, -terīus the other |
| nūllus no, none | ūllus any | neuter, -trīus neither |
| sōlus alone | ūnus one | uter, -trīus which (of two) |
Of these, the singular is thus declined.
a. The plural of these words is regular, like that of bonus (§ 110).
b. The genitive in -īus, dative in -ī, and neuter in -d are pronominal in origin (cf. illīus, illī, illud, and § 146).
c. The i of the genitive ending -īus, though originally long, may be made short in verse; this occurs often in alterius and regularly in utriusque.
d. Instead of alīus, alterīus is commonly used, or in the possessive sense the adjective aliēnus, belonging to another, another's.
e. In compounds—such as alteruter—sometimes both parts are declined, sometimes only the latter. Thus, alterī utrī or alterutrī, to one of the two.
Note— The regular genitive and dative forms (as in bonus) are sometimes found in some of these words.
gen. and dat.( f.) aliae
dat. (m.) aliō
Rare forms are alis and alid (for alius, aliud).