334. Some liquid and mute verbs take -η:ε- instead of -θη:ε- as passive suffix; an -ε- in the verb stem usually becomes -α-.
στέλλω (στελ-, σταλ-) send, ἐ-στάλ-ην
335. The inflection is like that of the θη- passive, except that the imperative ending -θι is not changed (synopsis, § 336, below).
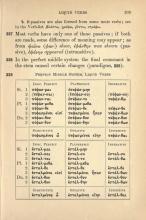
336. Synopsis of φαίνω (φαν-) show
| Liquid Aorist | Α-Perfect | Η-Passive | |
| Ind. | ἔφηνα | πέφηνα ἐπεφήνη |
ἐφάνην |
| Subj. | φήνω | πεφήνω | φανῶ |
| Opt. | φήναιμι | πεφήνοιμι | φανείην |
| Imptv. | φῆνον | --- | φάνηθι |
| Inf. | φῆναι | πεφηνέναι | φανῆναι |
| Part. | φήνᾱς | πεφηνῶς | φανείς |
a. The future passive is formed regularly (§ 310).
φανήσομαι, φανησοίμην, φανήσεσθαι, φανησόμενος
b. H- passives are also formed from some mute verbs; see in the Verb-list βλάπτω, γράφω, ῥῑ́πτω, στρέφω.
337. Most verbs have only one of these passives; if both are made, some difference of meaning may appear.
φαίνω (φαν-) show
ἐφάνθην was shown (passive)
ἐφάνην appeared (intransitive)