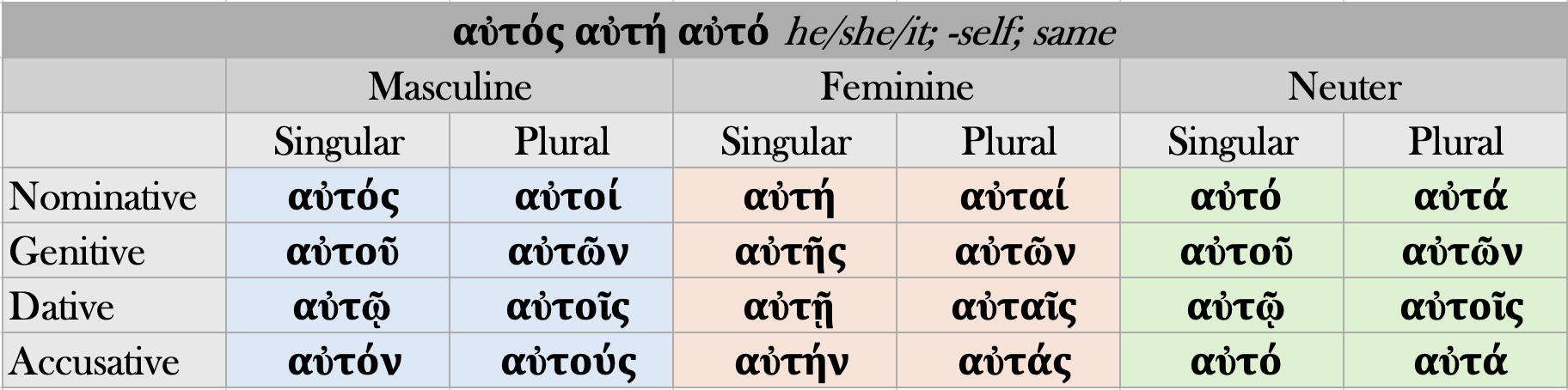
11.3 Our first pronoun is the Greek equivalent he/she/it (though see below). Greek uses a single pronoun for all of these, and declines it by gender, number, and case. While the definite article has the stem τ-, this pronoun has the stem αὐτ-. The forms of αὐτός use the same endings with one exception: The masculine nominative singular of the pronoun ends in –ς. The accent pattern is also similar to that of the definite article (S 327, G 198); the inflected forms have an ultima “circumflex belt”: nominative and accusative receive an acute, while genitive and dative receive a circumflex.
11.4 Depending on its placement in a sentence, αὐτός αὐτή αὐτό has three possible translations (S 328, G 199).
1. He/she/it
When the pronoun is standing on its own in any case except for the nominative, it is used as a 3RD PERSON PERSONAL PRONOUN. The form of the pronoun must correspond in gender, number, and case to the noun that it is replacing.
- οἱ ἄρχοντες διδόασι τὸ ὕδωρ τοῖς παισίν.
- Τhe rulers are giving water to the children.
- οἱ ἄρχοντες διδόασιν αὐτὸ αὐτοῖς.
- The rulers are giving it to them.
When this pronoun is used on its own in the NOMINATIVE case, it is emphatic and reflexive, much like ἐγώ, ”I,” is emphatic when used in a Greek sentence. It is also emphatic if a form of the pronoun is used as an ADJECTIVE in the PREDICATE POSITION (see definition below) to modify a noun of any case.
- ἀποδίδομεν τὰ χρήματα, ἀλλ’ οὐκ αὐτοὶ ἀποδιδόασιν.
- We give money back, but they themselves do not give (it) back.
- αὐτοὶ is in the NOMINATIVE case.
- οἱ ἄρχοντες αὐτοὶ διδόασιν αὐτὸ τὸ ὕδωρ τοῖς παισὶν αὐτοῖς.
- The rulers themselves give water itself to the children themselves.
- αὐτοὶ/αὐτὸ/αὐτοῖς are adjectives in the PREDICATE position.
When this pronoun is used instead as an ADJECTIVE in the ATTRIBUTIVE POSITION (see definition below), it means “same.”
- οἱ αὐτοὶ ἄρχοντες διδόασι τὸ αὐτὸ ὕδωρ τοῖς αὐτοῖς παισίν.
- The same rulers give the same water to the same children.
- αὐτοὶ/αὐτὸ/αὐτοῖς are adjectives in the ATTRIBUTIVE position.
- The same rulers give the same water to the same children.
- οἱ αὐτοὶ ἄρχοντες διδόασι τὸ αὐτὸ ὕδωρ τοῖς παισίν αὐτοῖς.
- The same rulers give the same water to the children themselves.
- αὐτοὶ/αὐτὸ are adjectives in the ATTRIBUTIVE position.
- αὐτοῖς is an adjective in the PREDICATE position.
- The same rulers give the same water to the children themselves.
- ATTRIBUTIVE vs. PREDICATE POSITION
-
An adjective is considered in an ATTRIBUTIVE POSITION when it modifies a noun with a definite article, and the adjective directly follows the definite article. For example: ἡ αὐτὴ πατρίς.
An adjective is considered in the PREDICATE POSITION if the adjective precedes the article or follows the article and noun. For example: ἡ πατρὶς αὐτή or αὐτὴ ἡ πατρίς. More on the significance of the attributive and predicate positions of adjectives is discussed in later lessons.